
Saturday and Sunday - CLOSED

Longwood, Fl 32779
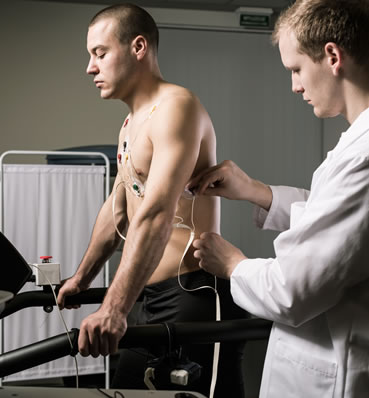
We use cardiac stress testing to detect the presence of heart disease
Compares coronary circulation at rest with circulation during activity.
Can be induced physically or via drug
Measures plaque buildup in arteries, and can help predict heart attacks.
We offer three forms of stress testing: Nuclear, PET Scan and Stress Echo.
TEST PREPERATION:
Understanding the Cardiac Stress Test:
– Purpose: The test measures how well your heart handles physical activity, helping to detect
coronary artery disease or assess your heart?s function before surgery.
– Procedure: You?ll walk on a treadmill or pedal a stationary bike while your heart rate, blood
pressure, and electrocardiogram (ECG) are monitored. The intensity of the exercise will gradually
increase.
– Types of Stress Tests: Exercise Stress Test and Pharmacologic Stress Test (if you cannot
exercise).
Preparation for the Stress Test:
1. Consult Your Doctor:
– Medication Instructions: Ask your doctor if you should take your regular medications before the
test. Some medications might need to be stopped.
– Dietary Restrictions: Avoid caffeine and certain foods for 24 hours before the test if instructed.
2. Fasting:
– No Eating or Drinking: Avoid food, drink (except water), or smoking for 2-4 hours before the test to
ensure accurate results.
3. What to Wear:
– Comfortable Clothing: Wear loose, comfortable clothing suitable for exercise, like athletic wear.
– Footwear: Wear comfortable shoes, such as sneakers, that are appropriate for walking or running.
4. Bring the Following:
– Medications: Bring a list of your current medications or the actual medications themselves.
– Identification and Insurance: Bring your ID and insurance information.
– Support: Consider bringing someone to drive you home afterward, especially if you feel tired or
lightheaded after the test.
What to Expect During the Test:
– Initial Setup: Electrodes will be attached to your chest to monitor your heart?s electrical activity.
Your blood pressure and heart rate will also be monitored.
– Warm-Up: The test begins at a slow pace, and the intensity will gradually increase. You may be
asked to walk faster or on an incline.
– Monitoring Symptoms: Inform the medical team if you experience chest pain, shortness of breath,
dizziness, or other unusual symptoms.
– Duration: The test typically lasts between 10 to 15 minutes, depending on your physical condition
and how your heart responds.
– Cool-Down: After the test, you’ll walk slowly for a few minutes to cool down while your heart rate
and blood pressure continue to be monitored.
After the Test:
– Rest and Hydration: You might feel tired or lightheaded after the test. Take some time to rest and
drink water.
– Results: Your doctor will review the test results and discuss them with you, including any follow-up
steps if needed.
Risks and Considerations:
– Low-Risk Procedure: A cardiac stress test is generally safe, but there?s a small risk of
complications such as irregular heart rhythms, dizziness, or chest pain.
– When to Seek Help: Contact your doctor or seek emergency medical help immediately if you
experience significant discomfort, shortness of breath, or severe chest pain after the test.
Copyright 2024. All rights reserved.